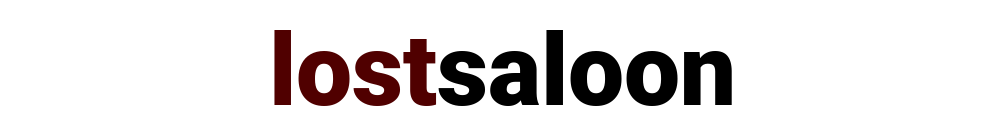how to configure proxy server in kde
Depending on the network you are connected to, you may need to configure a proxy server in order for you to connect to the internet. A proxy server is not a part of every network and is not a required component of a network. Large networks, such as corporate networks usually have a proxy server that allows the network traffic to be managed better.
It is very unlikely that you will have a dedicated proxy server on your home network, but there are several advantages in having a proxy server. You could install a proxy server such as polipo or squid to get some of the advantages of a web proxy. Something like privoxy can help with content manipulation. If you use a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or an Anonymising Proxy such as Tor, then you will be using a proxy server as well.
Almost all applications that interact with the outside network will have the ability to configure proxy in a graphical way. Some examples are web browsers such as Mozilla Firefox or Chrome. Many linux command line applications such as curl also provide this ability, albeit using the command line options.
Instead of configuring every single application with the proxy server settings, you have the ability to set the proxy server system wide at the desktop environment level. You can then configure the applications to use the system configuration. This allows you to quickly change your network settings instead of having to modify every single application.
In KDE, You can configure your system wide proxy at application level in the System Settings application. All desktop applications will then be able to read these values and use them, unless it is overridden.
- Open System Settings dialog either from the menu or command line
- Click on Settings under the Network section
- Click on Proxy section on the left of the pane
Now, you have several different ways to set your proxy
- No Proxy: This allows you to connect directly without a web proxy
- Detect proxy configuration automatically: This option allows you to use the WPAD (web proxy auto discovery) protocol to fetch the proxy configuration file.
- Use proxy auto configuration URL: You can specify a proxy configuration file or proxy script file using this method. (eg: http://wpad/wpad.dat)
- Use system proxy configuration: Many systems use environment variables such as HTTP_PROXY, FTP_PROXY, HTTPS_PROXY etc to configure proxy at the system level. If your system is configured using this method, then you choose to use the same values at the KDE level.
- Use manually specified proxy configuration: Manually specify the server configuration including the server name, port and any authentication you need to connect to the proxy.
Once you have modified or added/selected the configuration, Save or Apply the modified configuration.
You will have to restart some of the applications for the modified configurations to take effect. Now, every time you need to modify or change your proxy server you will need to modify the configuration only at the environment level rather than the application level.
For example in Mozilla Thunderbird, you can set your network connection to Use system proxy settings.
Configuring the proxy in this fashion still gives you the ability to modify the proxy configuration at an application level as well, just in case you want to bypass the proxy or use a different proxy for just a few application. So, the KDE level configuration works more or less as a default configuration.